1.3. Consonants ✅
1.3.1. What Is a Consonant?
A consonant is a speech sound that is produced by partially or completely blocking airflow in the vocal tract, such as with the tongue, lips or throat.
Three elements, or more specifically, articulatory features, define a consonant:
- Place of Articulation
The place of articulation is the location in the vocal tract where a consonant sound is produced. It is determined by the interaction between an active articulator (such as the tongue or lips) and the passive articulator (such as the hard palate or alveolar ridge). As the names suggest, active articulators are the organs capable of voluntary movement, whereas passive articulators are stationary, which means that they do not move during speech production.
- Manner of Articulation
The manner of articulation is how airflow is restricted or modified as it passes through the vocal tract during the production of a sound.
- Voicing
Voicing refers to the vibration of the vocal cords during the production of the sound. Consonants can be voiced (with vibration) or voiceless (without vibration).
1.3.2. Consonantal Inventory
General View
| CONSONANTS | Bilabial | Labio-dental | Dental | Alveolar | Post-alveolar | Palatal | Velar / Uvular | Glottal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | /m/ | /n/ | /ɲ/ | |||||
| Occlusive | /p/ /b/ | /t/ /d/ | /k/ /g/ | |||||
| Affricate | /ʦ/ /ʣ/ | /ʧ/ /ʤ/ | ||||||
| Fricative | /f/ /v/ | /θ/ | /s/ /z/ | /ʃ/ [ʒ] | [x] [ʁ] | [h] | ||
| Approximant | [β] | [ð] | /j/ [ɥ]1 | [ɣ] /w/2 | ||||
| Simple rhotic | /ɾ/ | |||||||
| Multiple rhotic | /r/ | [R] | ||||||
| Lateral | /l/ | /ʎ/ |
Allophones Only
The table below shows phonemes with associated allophones (regional variants and assimilations).
| CONSONANTS | Bilabial | Labio-dental | Dental | Alveolar | Post-alveolar | Palatal | Velar / Uvular | Glottal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | /m/ | /ɱ/ | /n̪/ | /n/ | /n̠/ | /ɲ/ | /ŋ/ | |
| Occlusive | /b/ | /d/ | /g/ | |||||
| Affricate | ||||||||
| Fricative | /s/ /z/ | |||||||
| Approximant | [β] | [ð] | [ɣ] | |||||
| Simple rhotic | /ɾ/ | |||||||
| Multiple rhotic | /r/ | |||||||
| Lateral | /l̪/ | /l/ | /l̠ʲ/ | /ʎ/ |
1.3.3. Places of Articulation
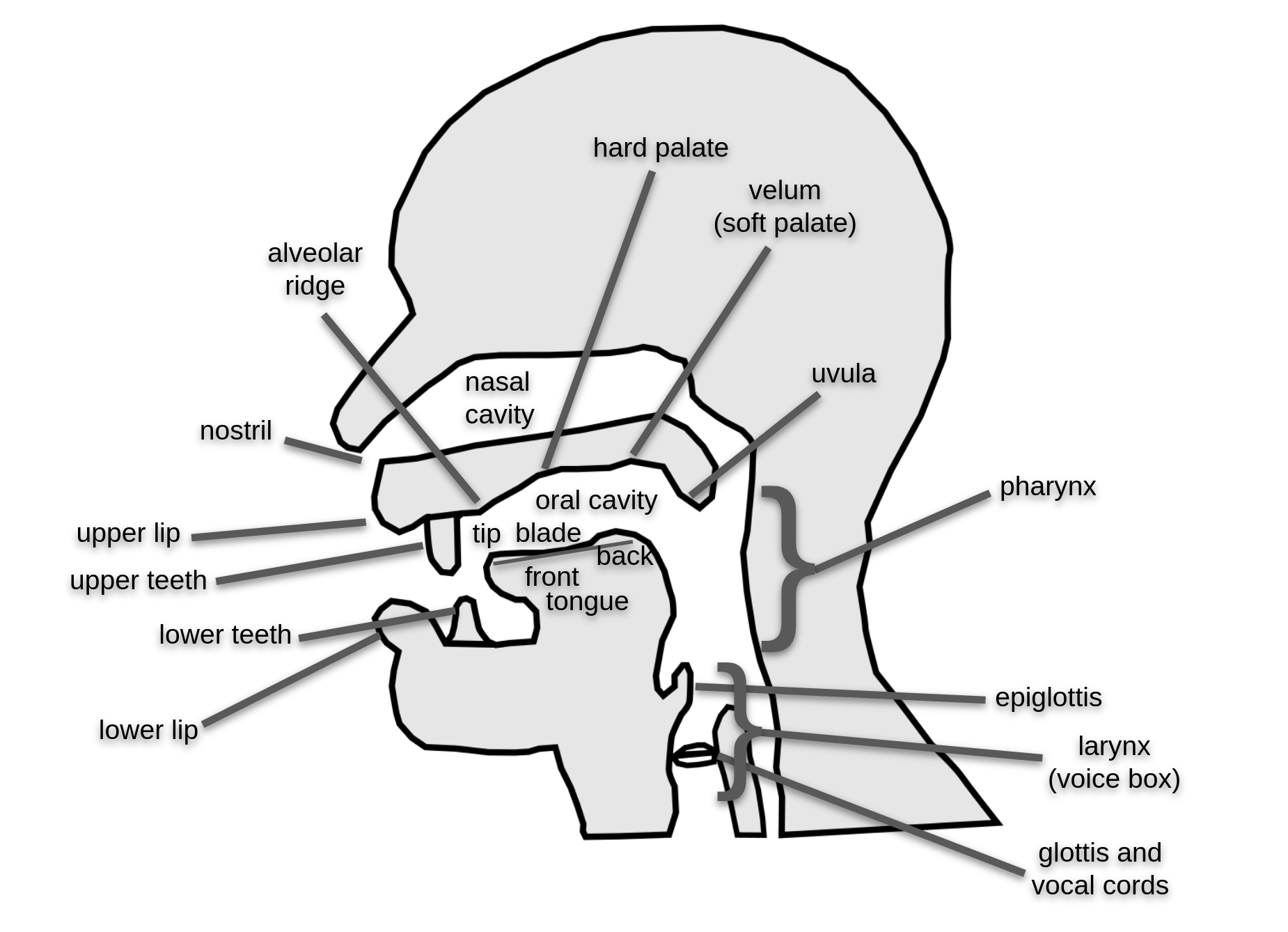
| Place of Articulation | Active Articulator | Passive Articulator |
|---|---|---|
| Bilabial | Lower lip | Upper lip (usually moves also) |
| Labiodental | Lower lip | Upper teeth |
| Dental | Tongue blade or tongue tip | Upper teeth |
| Alveolar | Tongue blade or tongue tip | Alveolar ridge |
| Post-alveolar | Tongue blade or tongue tip | Just behind the alveolar ridge |
| Palatal | Tongue body | Hard palate |
| Velar | Tongue body | Soft palate (also known as the “velum”) |
1.3.4. Manners of Articulation
| Manner of Articulation | Description |
|---|---|
| Nasal | The oral tract is blocked while the velum is lowered to allow air to escape through the nose. |
| Occlusive | The active articulator touches the passive articulator, completely blocking airflow in the vocal tract. |
| Affricate | The oral tract is completely blocked, but the velum is lowered to allow air to escape through the nose. |
| Fricative | The active articulator gets close enough to the passive articulator while not completely touching. The airstream is obstructed to some degree and friction remains audible (turbulent airflow). The air is forced through a narrow constriction in the vocal tract. |
| Approximant | The active articulator approaches the passive articulator, but not close enough to produce turbulent airflow (audible friction). They are intermediate sounds between vowels and obstruent consonants (occlusives, fricatives and affricates). This manner of articulation includes semi-consonants, but not exclusively. |
| Vibrant (Tap and trill) | The airstream meets with the rapid movement of the tongue. For taps, the tongue tip gives a single light tap to the roof of the mouth. For trills, the tongue tip vibrates against the roof of the mouth in a current of air. |
| Lateral | The center of the tongue blocks airflow such that air must flow along the sides of the tongue. |